The CSS ‘position’ property is a fundamental aspect of page design in CSS.
Read on to get a breakdown of how this important component works!
static
If the position property is not set, it is automatically ‘static’. Setting the left, right, bottom, top and z-values in static mode will have no effect. It will just exist within the normal page flow.
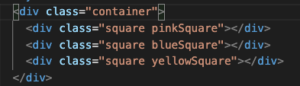
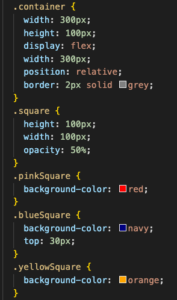

Notice how the blue block has a ‘top’ value of 30px, but the blue block has the same vertical position as the other blocks.
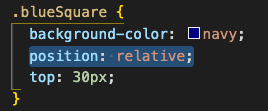
relative
Now things start to get fun! If left, right, top, bottom or z-values are set for an element in relative mode, the adjustments will be applied relative to the elements default position.

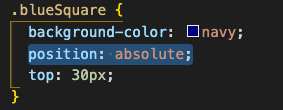
absolute
When an element’s position attribute is set to absolute, its position is determined relative to the container it is within (that or its closest position ancestor). It is taken out of the normal flow of elements in the document.
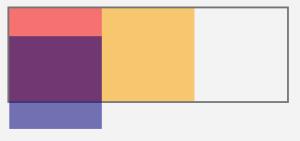
fixed
Elements with the fixed position are positioned relative to the viewport. They are taken out of the normal flow of the elements in the document.
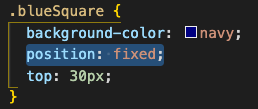

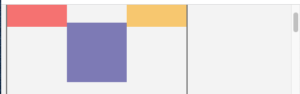
sticky
Sticky positioning means that an element will behave as though it is relative, until it crosses a positional threshold, and then it is treated as fixed. It is also taken out of the normal flow of the document.
References:
- httpss://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/CSS/position